Electric Vehicles (EV) despite being a greener, smoother and cheaper mode of transport,you will need a minimum of 6-8 hours to charge a typical EV. Many companies like Tesla, EVgo, charge point etc have already acknowledged this problem by setting up charging stations around the country. With countries like Netherland, who promised to give up petrol engine by 2035 it is sure that the roads of future will be replaced with EVs over internal combustion engines and a lot of EV charging stations would pop up around us.

What's the difference between AC or DC charging?
There are two 'types' of electricity supply: AC and DC. Here a list of comparison points to explain the differences:
AC charging
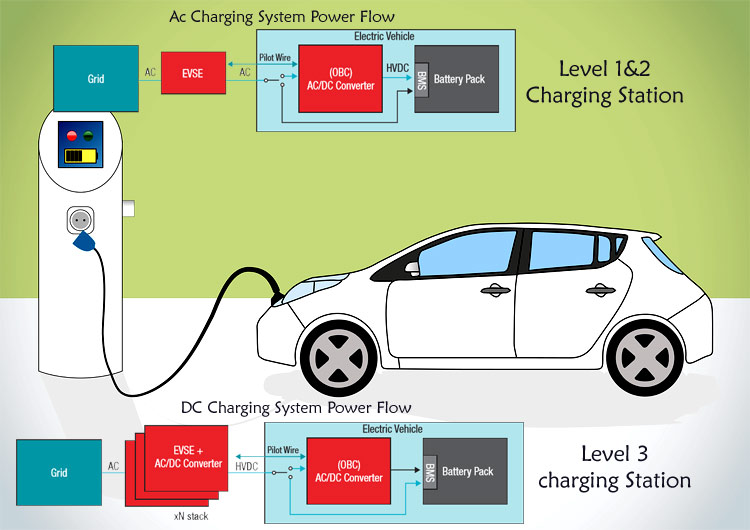
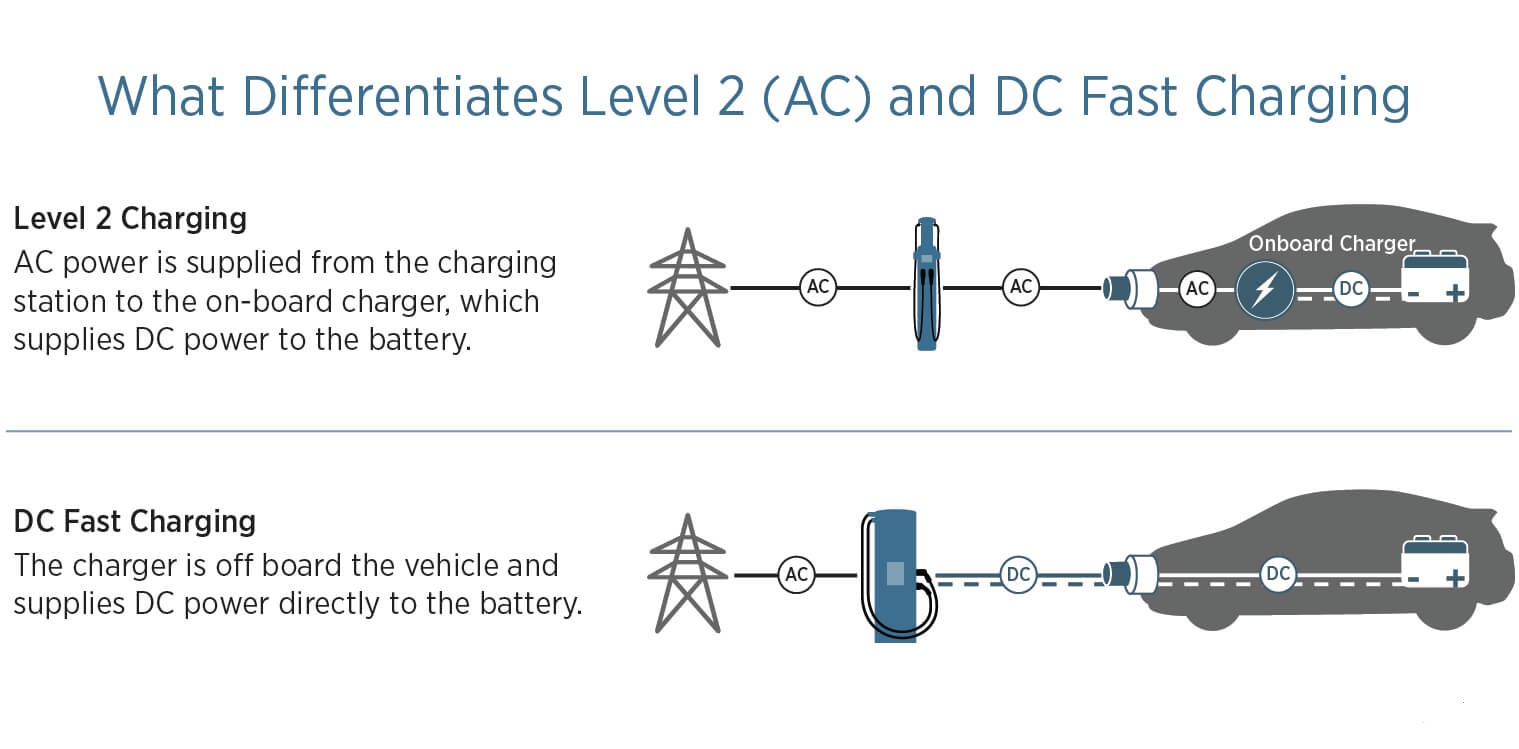
When charging an electric car with alternating current, the car's on-board system (also called the on-board charger) is used and it takes care of the conversion of outlet current into battery current. It therefore receives alternating current (AC) and converts it into direct current (DC), which is then sent to the car battery.
The key parameter when choosing an electric car is the capacity of this on-board (built-in) charger, because the car's charging speed depends on how fast this on-board system can receive the alternating current from the source and also on how many phases it is able to use.
AC charging station
When charging with AC stations, the electrical grid is connected to the on-board charger.
The AC charging station thus regulates the charging according to the current possibilities of the house or the charging point, so that the network is not overloaded.
The main advantage of AC stations is that they are affordable. They are 7x-10x cheaper than DC charging stations with the same performance. Their other advantage is that they are much more widespread due to their lower price. At the same time, they are significantly smaller and their installation is simpler, faster and less expensive. Thanks to their characteristics, AC charging stations are also suitable for home installation and night charging
DC charging
DC charging, or so-called fast charging, is done using a DC charging station, which can change the alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), it then "bypasses" the on-board charger of the electric car and sends this direct current via Battery Management System (BMS) to the battery, as instructed by the vehicle's charging control system.
Charging is therefore not limited by the power of the on-board charger and so it can be much faster.
DC charging station
A DC charging station is technologically much more complex and many times more expensive than an AC charging station and moreover it requires a powerful source. In addition, a DC charging station must be able to communicate with the car instead of the on-board charger in order to be able to adjust the output power parameters according to the condition and capability of the battery.
Mainly due to the price and technological complexity, we can count significantly fewer DC stations than AC stations. Currently there are hundreds of them and they are located on the main arteries.
A DC installation requires a lot of power from the grid (around 125 A). This makes its costs (production, installation and operation) quite high, resulting in higher tariffs for charging. However, as it usually allows for much faster charging, it is the preferred charging method to quickly recharge during long-distance trips (for cars that support DC charging). This type of chargers is mostly found along highways, rather than at home or business locations.
Charging tariffs
Regardless of AC or DC, generally the costs (production, installation and operation) and therefore the charging tariffs will go up with increasing power of the chargepoint.
Note that this does not take into account the charging speed of your car. So if your car can not charge on high capacity, but you’re connected to a high output AC chargepoint (e.g. 43 kWh) you may pay a very high price for a low amount of energy.
What type of charging should you choose?
“Normal” AC charging is preferred for long parking . It's ideal for charging your car at home or work . DC charging, on the other hand, is more common near highways or at public charging stations, where you don't have much time to recharge. whereas “fast” DC charging is used when vehicles are parked less than 2 hours. It is offering new possibilities for customers since it allows not only fast charging but also bidirectional charging.
EEVC 7KW single-phase and EEVC 11KW three –phase Wallbox AC Charging Station are new generation of intelligent products launched by Aswich solve the pain points of home charging.
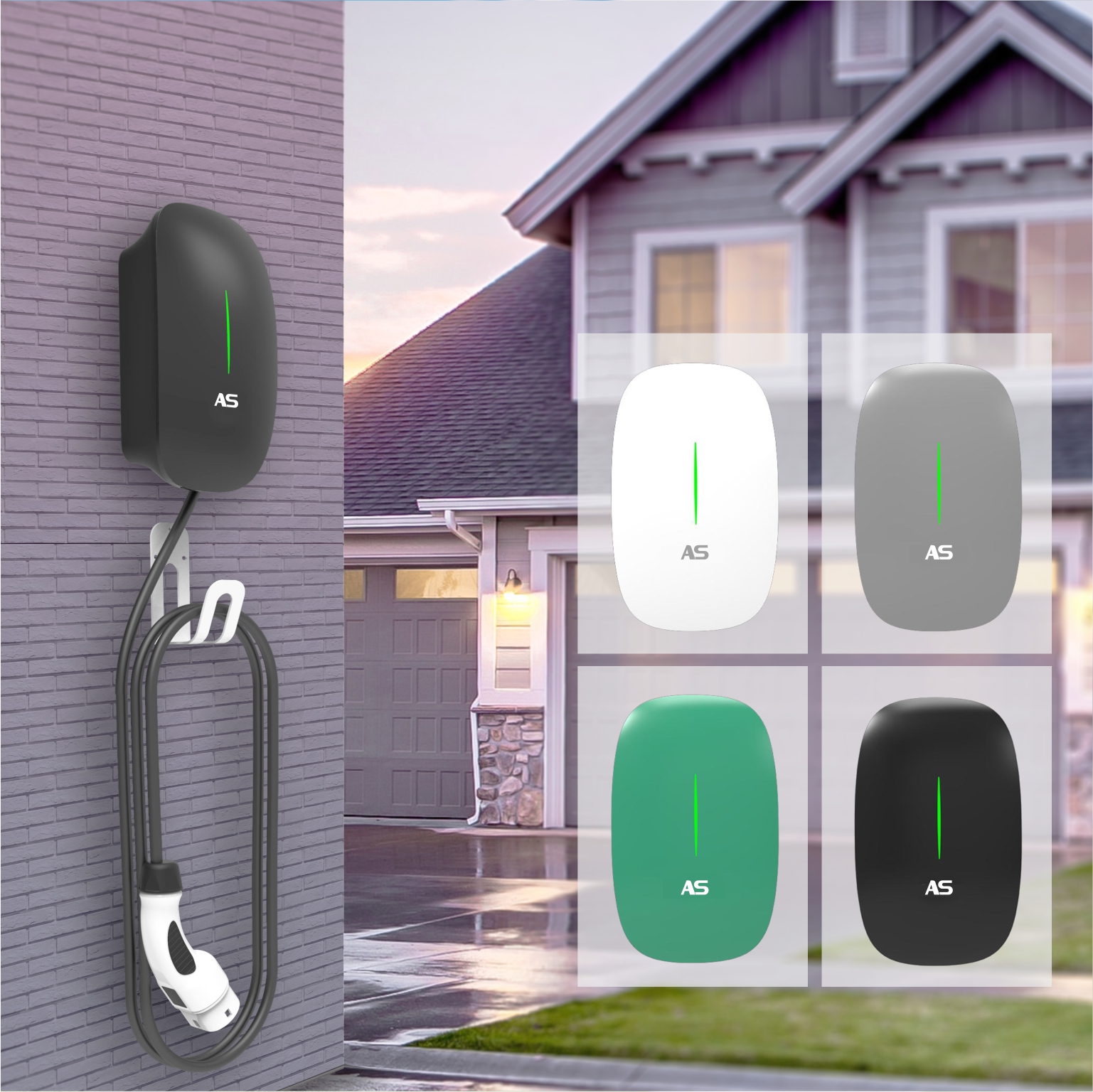

Innovativeness
Minimal size, streamline design
Home use with intelligent App control
Intelligent Control
Wireless communication (WiFi/Bluetooth)
OCPP communication protocol with the backend
Use the mobile app to start the charging pile to charge the vehicle
Flexible Option
The type 2 (IEC 62196-2) charging connector makes highly flexible and compatible with all electric vehicles.
Wall-mounted or floor-stand installation
